September 17, 2024
BlogThe comparison between gantry robots and 6-axis robots?
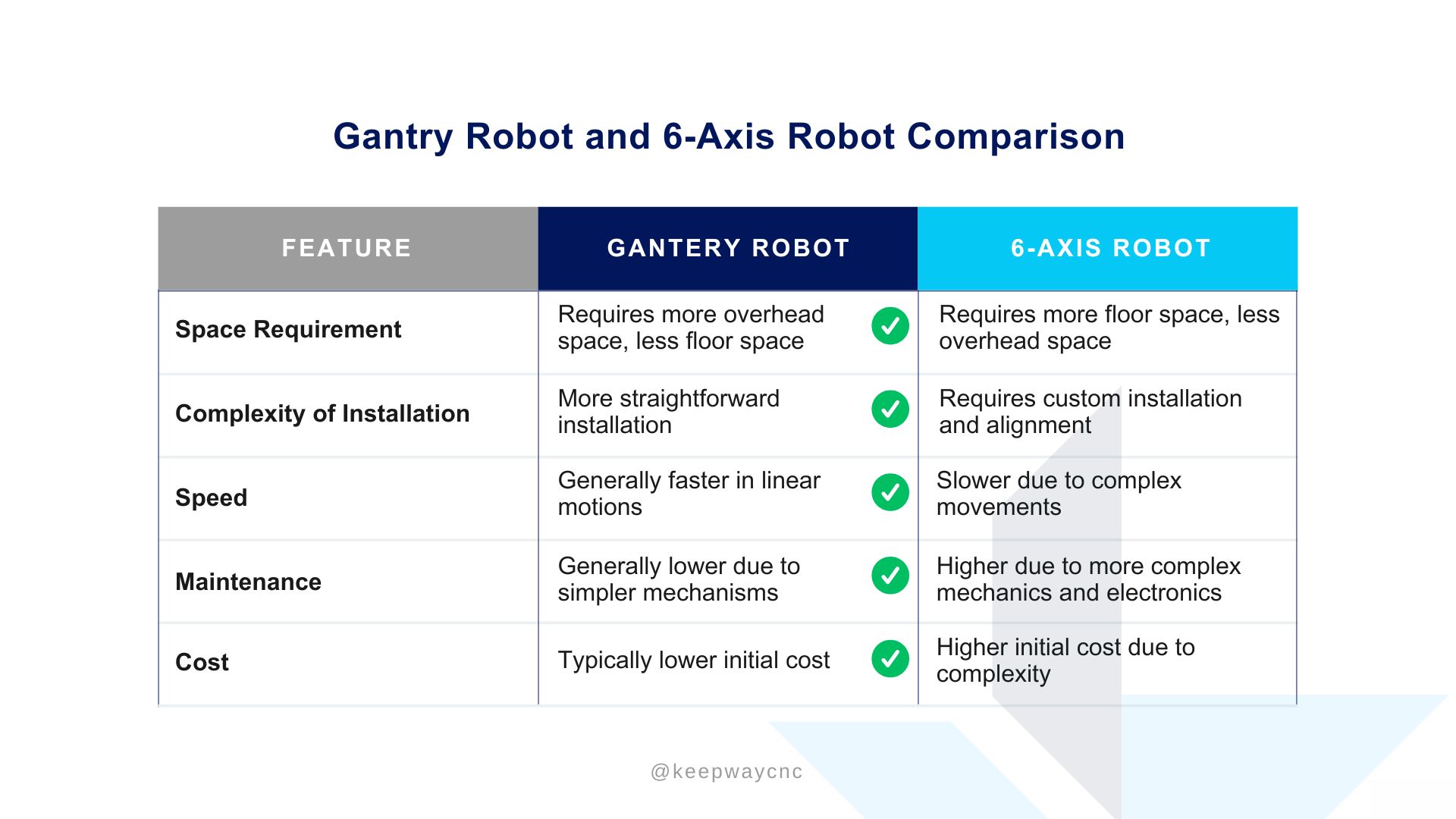
The comparison between Gantry Robots and 6-Axis Robots highlights their strengths and suitability for various industrial applications.
Here’s a breakdown based on key factors:
-
Space Requirement:
- Gantry Robot: Typically requires more overhead space but occupies less floor space. This makes it ideal for facilities with limited floor area and abundant vertical clearance.
- 6-Axis Robot: Conversely, this robot demands more floor space while needing less overhead room. Its compact, floor-mounted design can be beneficial in environments where vertical space is restricted.
-
Complexity of Installation:
- Gantry Robot: Known for its simpler installation process, the gantry robot is straightforward to set up and integrate into production lines. This ease of installation allows companies to quickly deploy it without extensive alignment requirements.
- 6-Axis Robot: Installation for the 6-axis robot can be more complex due to its sophisticated configuration. Custom alignment and calibration are often necessary, which can increase setup time and costs.
-
Speed:
- Gantry Robot: Generally faster in linear movements due to its direct path. It’s well-suited for tasks requiring high-speed, repetitive linear motion, enhancing efficiency in specific operations.
- 6-Axis Robot: Due to its complex, multi-directional movement capabilities, the 6-axis robot operates at a slower speed. However, it offers enhanced flexibility, which can be beneficial for intricate or multi-angled tasks.
-
Maintenance:
- Gantry Robot: With a simpler mechanical structure, maintenance is relatively easy and often less costly. The straightforward design translates to fewer components that may need repairs or replacements.
- 6-Axis Robot: The complexity of the 6-axis robot, with its advanced mechanics and electronics, leads to higher maintenance demands. Maintenance procedures may also require specialized skills, adding to long-term operational costs.
-
Cost:
- Gantry Robot: Generally, gantry robots are more cost-effective, especially in terms of initial investment. Their straightforward design and ease of maintenance contribute to lower overall costs.
- 6-Axis Robot: The initial cost is typically higher due to the robot’s advanced technology and flexibility. The complexity of the robot adds to both initial setup and potential long-term maintenance costs.